Ever wake up with body aches and pains and wonder what you did? Inflammation could be the source!
But here’s a surprising fact. Inflammation isn’t necessarily a bad thing for your body. In fact, it can be a good thing in some cases. That’s because inflammation is your body’s way of defending itself from simple mosquito bites to full-on attacks to key body systems.
It’s important to note that inflammation can affect you at any age. It isn’t just limited to the aches and pains of getting older and dealing with arthritis. Athletes, busy moms and dads, college students, and even kids can suffer the side effects of inflammation.
That’s why we’re taking a deep dive into everything you need to know about inflammation including what causes it, the difference between acute and chronic cases, how it affects each system’s function, and steps you can take to reduce inflammation fast.
What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is your body’s way of calling in the superheroes. When your body detects something foreign like bacteria or a virus, it triggers an immune response and boosts its production of white blood cells and cytokines. The mission? Send antibodies, proteins, and extra blood flow to the affected area to fight or eliminate whatever injury, infection, or toxin that is keeping your body from functioning at its best. The technical term for this type of inflammatory response is acute inflammation.
Typically, acute inflammation usually only lasts a few hours or days at most and can make the affected area sore, red and sometimes swollen. This can be a bit bothersome in the short term, but overall it’s a pretty cool snapshot at how our body is made to heal itself. If symptoms last longer than a few days, however, that’s when you enter chronic stages and when major health issues can start to pop up.
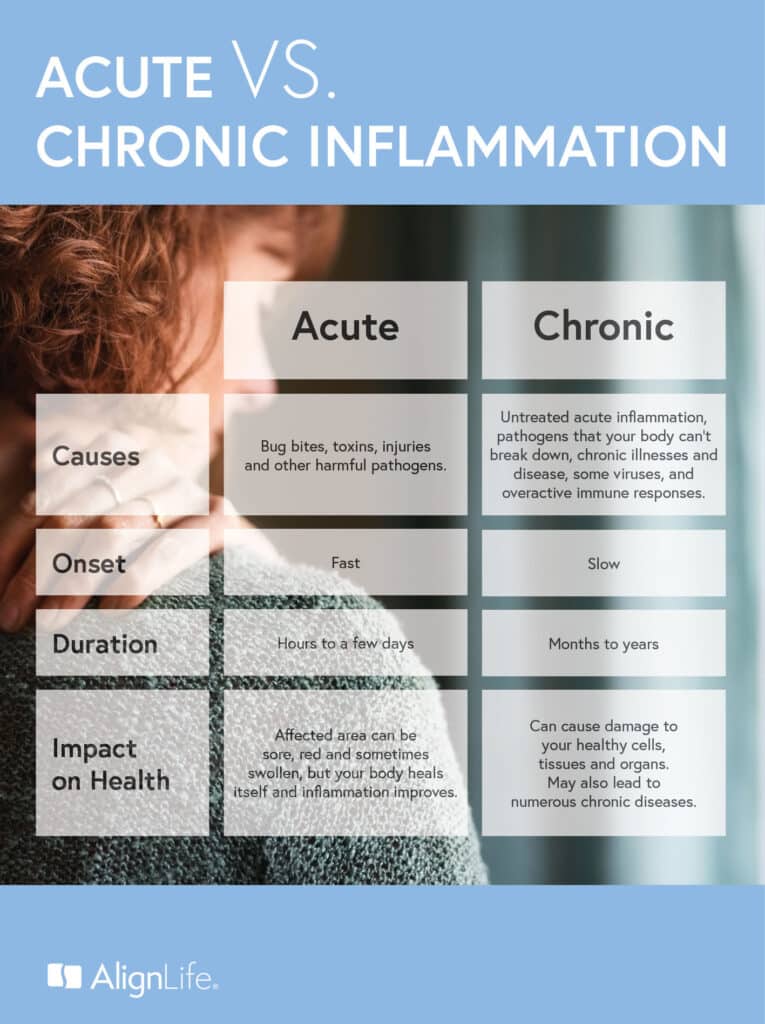
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is a whole different beast than acute inflammation and one of the key reasons it gets a bad rap. That’s because with chronic inflammation, you can experience mild to severe symptoms for months if not years. This type of sustained low-level inflammatory response irritates your blood vessels and puts your body in a constant state of alert.
Over time, chronic inflammation can cause damage to your healthy cells, tissues and organs. In fact, researchers are now even linking or finding evidence that chronic inflammation could be playing a part in numerous chronic diseases. Some of the disease inflammation could trigger include:
- Heart disease (heart attacks and strokes)
- Cancer
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Digestive issues
- Type 2 diabetes
- Rheumatoid arthritis and other joint pain
- Psoriasis and other skin conditions
- Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s disease
What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
While there is not one set reason for chronic inflammation to set in, we do know there are several conditions or factors that could cause it to progress to chronic levels. Factors that can increase your risk include:
- Not managing or treating acute inflammation from an illness or injury
- Living with an autoimmune disorder (your immune system literally thinks your healthy tissues are invaders constantly attacks)
- Having long-term exposure to irritants like toxins, chemicals, smoke and more
- Having a sensitivity to an external irritant resulting in an allergy
- Not getting enough sleep
Not every situation listed above will develop into chronic inflammation. However, experts believe that a range of factors, such as older age, smoking, obesity, diets rich in unhealthy fats and processed sugars, alcohol, sleep issues and chronic stress can all contribute or increase your risk of developing chronic inflammation.
Signs of Chronic Inflammation
Some common (and not so common) symptoms or health problems from chronic inflammation include:
- Body pain, arthralgia, myalgia
- Chronic fatigue and insomnia
- Depression, anxiety, and mood disorders
- Constipation, diarrhea, and acid reflux
- Weight gain or weight loss
- Frequent infections
- Balance problems
- Insulin resistance
Your doctor can also look for certain biomarkers (C-reactive protein [CPR] and erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR]) that can be found on X-rays or blood tests.
Why Reducing Chronic Inflammation Matters
It’s becoming clear that more and more research is flagging inflammation as a contributing factor to many chronic diseases. That alone should make you want to take note, make some lifestyle changes, and work on preventing and reducing in your body.
On top of that, when your body is having an inflammatory response, the inflammation in your cells creates static that impacts how clearly your central nervous system communicates with the rest of your body. If one system isn’t functioning to its optimum potential, your overall health and how you feel and function throughout your day can and will take a hit.
Just look at the impact this can have:

- Pro-inflammatory cytokines can cause autoimmune reactions in the brain. Can lead to depression, autism, poor memory, Alzheimer’s disease, and MS.
- Inflammation in the heart, arteries and veins can lead to cardiovascular issues. Can lead to heart disease, stroke, anemia, and high blood sugar.
- Inflammatory cytokines can cause muscle pain and weakness. Can lead to carpal tunnel syndrome and myositis.
- Inflammation interferes with your body’s natural ability to repair bones.
Can lead to more bone fractures and osteoporosis. - Chronic inflammation impacts your skin health. Can lead to rashes, dermatitis, eczema, acne, psoriasis, wrinkles.
- Inflammation plays an important role in thyroid function. Can lead to thyroid and autoimmune diseases.
- Inflammation in the lungs can cause autoimmune responses. Can lead to allergies and asthma.
- Inflammation in the GI tract can cause damage to the intestinal lining. Can lead to GERD, Crohn’s disease, and Celiac disease.
- Inflammation restricts blood flow to the kidneys, decreasing function. Can lead to edema, hypertension, nephritis and kidney failure.
- Inflammation overtaxes your liver. Can lead to an enlarged liver, fatty liver disease and toxic build-up in the body.
How Chiropractic Can Help Reduce Chronic Inflammation
A trip to your local AlignLife Chiropractor can help you get inflammation under control fast. Not only will a chiropractic adjustment help make sure your spine is aligned, it reduces the pressure on your nerves, reduces pain from injuries, and helps promote a healthy nervous system. With a well-aligned spine, your body’s biomechanics also return to normal.
This is important because it stops the production of neuropeptides and cytokines – both of which are major regulators of your body’s immune and inflammatory response. We encourage you to reach out to your chiropractor to talk more about how regular chiropractic adjustments can move you beyond aches and pains and help you reach and maintain your health goals.

Top Ways to Reduce Inflammation Fast
Following an anti-inflammatory diet is one of the best ways to reduce inflammation in your body. A Mediterranean diet is a good guideline or you can tap into specific anti-inflammatory, magnesium-rich foods like leafy greens and veggies, kale, blueberries, avocados, mackerel, sardines (or other fatty fish), whole grains, and healthy fats. At the same time, it’s also important that you avoid foods that cause inflammation such as red meat, added sugars, fried foods, and more. And that’s just the beginning of what you can do to help.
In addition to an anti-inflammatory diet, there are also a few dietary supplements you can take that have been proven to help with inflammation. Turmeric and curcumin are two of the top and they’re a powerful combo when taken together. Both turmeric and curcumin are found in Aceva Mobility which we recommend because it helps improve overall joint function throughout your body by naturally reducing inflammation and pain with its powerful combination of turmeric and other anti-inflammatory herbal extracts. When you combine it with Aceva Joint Rescue — which features their signature blend of four joint-enhancing compounds that have been clinically tested and proven effective for those suffering from joint pain — you’ll not only get relief but start seeing improvements in how you move.




